Axal
Automatically refactor Java and C# monoliths into modern microservices architecture
Introduction
What is Axal?
Axal is a sophisticated AI-powered platform engineered to assist enterprises in revitalizing outdated monolithic software. It transforms these applications into flexible, modular systems like microservices by automating the intricate tasks of codebase analysis and restructuring. The platform intelligently charts out code dependencies, pinpoints architectural weaknesses such as circular dependencies and boundary breaches, and sequences refactoring efforts according to business value. Axal's AI independently executes code modifications, safeguarding quality with ongoing testing. This leads to speedier deployment of new features, diminished technical debt, and more cost-effective maintenance.
Key Features:
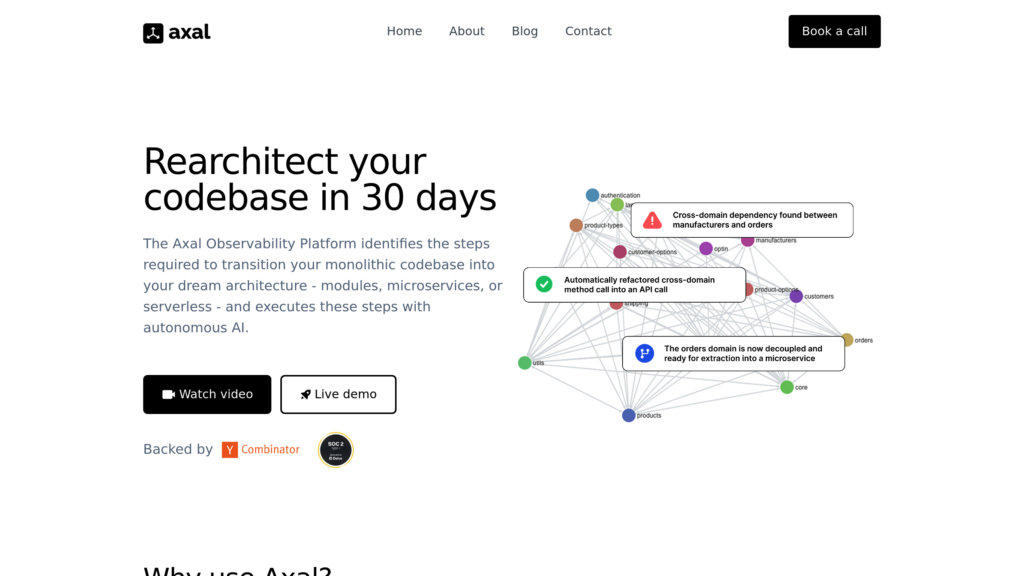
• Automated Codebase Analysis: Systematically examines both static code links and dynamic runtime data to chart business domains and illustrate the complete code structure for ultimate clarity.
• Prioritized Technical Debt Management: Uncovers structural problems, including circular dependencies, domain integrity issues, and overly complex classes, and ranks them based on strategic business objectives.
• AI-Enabled Restructuring: Utilizes artificial intelligence to independently resolve architectural impediments and reorganize code, with verification that all tests succeed both pre- and post-modification.
• Gradual Modernization Framework: Facilitates the 'strangler fig' approach by pinpointing and ranking specific application functions for step-by-step upgrade and renewal.
• Dynamic Code Adaptation: Automatically adjusts to continual code updates, removing the necessity for frequent manual re-architecting efforts.
• Deep-Dive Code Insights: Delivers comprehensive analysis of relationships within the codebase at both class and domain levels, supporting data-driven strategic choices.
Use Cases:
• Legacy System Modernization: Enables businesses to smoothly migrate substantial monolithic Java or C# applications to contemporary modular or microservices-based designs.
• Strategic Technical Debt Reduction: Provides development teams with clear, prioritized actions to manage and decrease architectural debt in line with company goals.
• Faster Feature Development: Automates structural code improvements, freeing developers to concentrate on creating new functionalities and accelerating time-to-market.
• Enhancing Code Scalability: Improves long-term maintainability and scalability by addressing architectural hurdles and promoting well-defined domain separations.
• Safe Refactoring Process: Lowers the risk of disrupting existing operations by validating code integrity through testing before and after AI-implemented changes.